Hernia Treatment
Home > General Treatments > Hernia Treatment
A hernia is a medical condition where an organ or tissue pushes through a weakened area in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This results in a visible bulge or lump, which can be painful and uncomfortable. Hernias can occur in various parts of the body, but they are most commonly found in the abdominal region, groin, and upper thigh.
While most hernias are not immediately life-threatening but they do not resolve spontaneously. Surgery may be necessary in some cases to prevent potentially dangerous complications associated with hernias.
We have team of best doctor dedicated to the treatment of hernias. With extensive experience and expertise, our doctor is at the forefront of diagnosing and managing various types of hernias. Our doctors are equipped with decades of experience, advanced medical knowledge and best facilities. Our doctor ensures optimal outcomes and patient satisfaction. Whether it's an inguinal hernia, hiatal hernia, or any other type, our doctor employs a comprehensive and personalized approach to provide top notch care. With a focus on patient well-being and compassionate treatment, we are the premier choice for individuals seeking the best hernia specialist in Lahore.
There are several types of hernias. These can be categorized based on their location and the area where the protrusion occurs.
The most common types of hernias are
Inguinal Hernia: This is the most prevalent type of hernia and occurs in the groin area. It happens when a portion of the intestine or the bladder pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, typically through the inguinal canal.
Hiatal Hernia: This type of hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes upward through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, often into the esophageal hiatus. It is common in individuals with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Incisional Hernia: These hernias develop at the site of a previous surgical incision, where the abdominal muscles may not have healed properly, creating a weakened spot.
Umbilical Hernia: Occurring around the navel (belly button), an umbilical hernia happens when a section of the intestine or fatty tissue protrudes through the abdominal wall near the umbilicus.
Femoral Hernia: This type of hernia occurs just below the inguinal ligament in the upper thigh, through the femoral canal. It is more common in females and may contain a loop of intestine.
Ventral Hernia: Ventral hernias develop in the abdominal wall, often at the site of a surgical scar. They can occur in various locations on the anterior abdominal wall.
Spigelian Hernia: A Spigelian hernia occurs along the semilunar line, a weakness in the abdominal wall between the rectus abdominis muscle and the lateral edge of the rectus sheath.
Epigastric Hernia: This type of hernia appears in the midline of the abdomen, between the sternum and the umbilicus, through a weak spot in the linea alba (a band of connective tissue).
Each type of hernia requires appropriate medical evaluation and treatment. If you suspect you have a hernia or experience symptoms like a visible bulge, discomfort, or pain in the affected area, it's essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and management.
Hernias are typically caused by a combination of factors that lead to increased pressure on a weak spot or opening in the muscle or connective tissue. The common causes of hernias include:
Congenital Weakness: Some people are born with a natural weakness in their abdominal wall or other areas of the body, making them more prone to developing hernias.
Aging: As people age, their muscles and connective tissues naturally weaken, increasing the risk of hernias.
Heavy Lifting: Engaging in activities that involve heavy lifting or straining can put significant pressure on the abdominal area, potentially leading to hernias.
Chronic Coughing or Sneezing: Frequent and forceful coughing or sneezing can strain the abdominal muscles and contribute to the development of hernias.
Obesity: Excess body weight can place additional pressure on the abdominal wall, making hernias more likely to occur.
Pregnancy: The pressure from the growing uterus during pregnancy can strain the abdominal muscles and lead to hernias.
Previous Surgery: Surgical incisions can weaken the surrounding tissues, increasing the risk of incisional hernias at the site of the previous operation.
Straining during Bowel Movements: Persistent constipation can strain the abdominal muscles, so it can contribute to hernia formation.
Chronic Lung Disease: Conditions that cause chronic coughing, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), can increase the risk of hernias.
Ascites: Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity can increase pressure on the abdominal wall and contribute to hernias.
It is important to note that some hernias may have no apparent cause and can develop spontaneously without any specific triggering event. Additionally, some factors, such as family history of hernias, connective tissue disorders, and multiple pregnancies, may increase an individual's susceptibility to hernia development.
Diagnosing a hernia typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes imaging studies. Here's how hernias are commonly diagnosed:
Medical History: Your doctor will begin by asking about your symptoms, including any visible bulges or lumps, as well as any pain or discomfort you may be experiencing. They will also inquire about your medical history, any previous surgeries, and risk factors that may contribute to hernia development.
Physical Examination: The doctor will perform a physical examination, focusing on the area where you suspect the hernia is located. They may ask you to cough or strain while they examine the area, as this can sometimes make the hernia more evident.
Imaging Studies: In some cases, doctor may order an ultrasound or a CT scan, to get a clearer view of the hernia and its location.
Inguinal Hernia Examination: For suspected inguinal hernias (groin hernias), your doctor may perform a special examination known as a "standing cough test" or "finger palpation test" to check for the presence of the hernia.
Endoscopy: If a hiatal hernia is suspected, an endoscopy may be performed. In this procedure, a flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth and into the esophagus and stomach to visualize the hiatal area.
It is important to note that not all hernias may be visible or easily detected during a physical examination. In some cases, hernias may be asymptomatic or cause only mild discomfort, and the diagnosis may be confirmed incidentally during routine medical checkups or imaging studies for other conditions.
The treatment of a hernia depends on several factors, including the type of hernia, its size, symptoms, and the individual's overall health.
Generally, there are two main approaches for hernia treatment:
Watchful Waiting: In some cases, especially when the hernia is small and not causing any symptoms, a "watchful waiting" approach may be adopted. This means the hernia is monitored regularly by a doctor to check for any changes or developments. If the hernia remains small and asymptomatic, surgical intervention may not be immediately necessary.
Wearing a truss can be beneficial in alleviating hernia symptoms in certain situations. A truss is a supportive undergarment designed to keep the hernia in place. However, it is crucial to consult with your doctor to ensure a proper fit and suitability before using a truss for hernia management.
Hernia Repair Surgery: If the hernia is symptomatic, enlarging, causing discomfort, or at risk of complications (such as strangulation), surgery is usually recommended to repair the hernia. The surgical procedure involves pushing the herniated tissue or organ back into its proper position and reinforcing the weakened abdominal wall with sutures, mesh, or other materials to prevent recurrence.
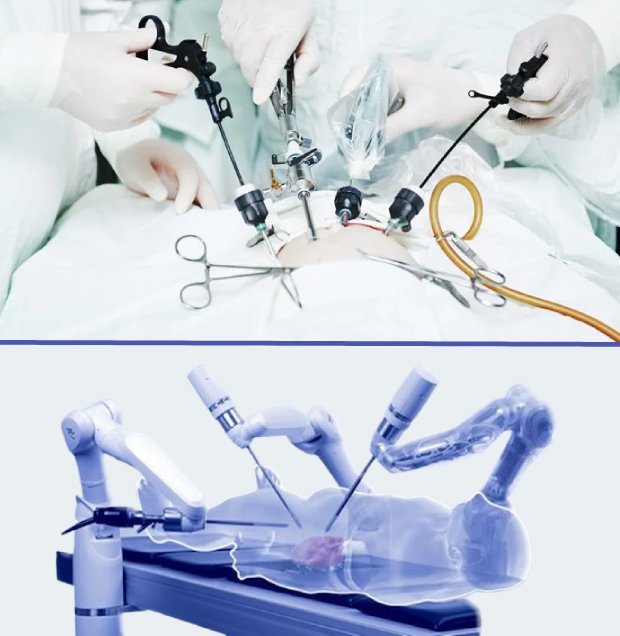
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: In this minimally invasive approach, the surgeon makes several small incisions and uses a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) and specialized instruments to repair the hernia from within the abdominal cavity. Laparoscopic surgery typically results in faster recovery, less postoperative pain, and minimal scarring.
It may not be possible to completely eliminate the risk of hernias, there are several steps you can take to reduce your chances of developing one:
While these measures can help reduce the risk of hernias, it is important to remember that some hernias may still occur due to factors beyond your control.
If you suspect you have a hernia during pregnancy, it is essential to visit Doctor. A doctor can evaluate the hernia's condition and assess any potential health risks.
In many cases, hernia repair can be postponed until after childbirth. However, if a small hernia that was present before or during pregnancy enlarges or causes discomfort, surgical repair may be recommended during the second trimester. It is important to note that hernias previously repaired may recur during later pregnancies due to the strain on weakened abdominal muscle tissue caused by pregnancy.
Cesarean deliveries can also lead to hernias. Incisional hernias may develop at the site of the cesarean delivery. As the incisions made in the abdomen and uterus during the procedure can create weakened areas. If you experience any symptoms or have concerns about a hernia during pregnancy or after childbirth, consult with your doctor for proper evaluation.
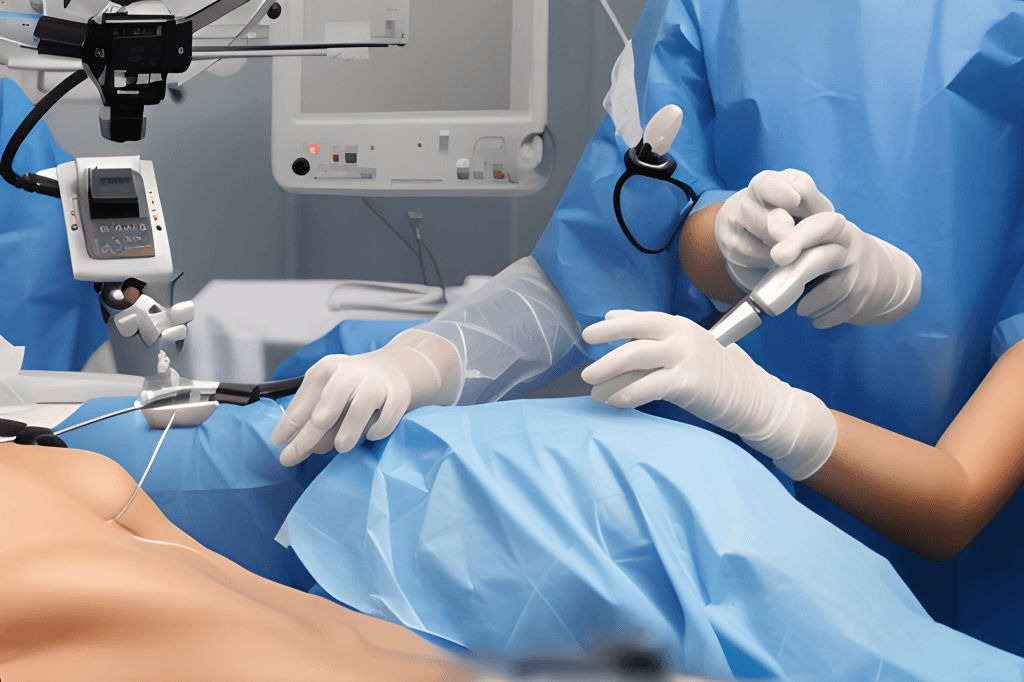
We are the best laparoscopic surgeon specializing in the treatment of hernias. Our highly skilled surgeon possesses vast expertise in performing laparoscopic hernia repairs in Lahore. We offer our patients state of the art minimally invasive solutions in Lahore. With a focus on precision and patient care, our surgeon employs advanced laparoscopic techniques to ensure successful outcomes and quicker recovery. Whether it's an inguinal, hiatal, or incisional hernia, our dedicated laparoscopic surgeon provides personalized treatment plans to address each patient's unique needs.
Contact UsCopyright @ . Design By Blizin Technologies